It is surprising to see that so many believe that when Google indexes web content (Caffeine indexer) it stores ranking information at the same time.
However, the Google search engine builds rankings instantly during the serving of organic results. And, it typically happens in milliseconds…impressive!
We know that consistently garnering top rankings in organic results can drive more quality traffic and lift a brand’s trust.
The question remains…
Is there a close to sure-fire way to affect how Google (and search engines in general) displays your web pages and properties at the top or on the first page of search results?
There is no easy answer… but subjects like crawling, indexation, topical alignment, semantic-lexical-logical words/phrases, relevancy, on-page and off-page tactics, authority and trust building are all important in this discussion. Clearly a lot to cover in ONE article.
However, this post is not a detailed or deeply instructive guide on how to impact all search ranking factors (there are 200 we know of).
Start With Optimizing The Crawl
Rather, we’ll discuss essential keys to success that begin with managing the search engine “crawl budget”. Or, as Google calls it internally: “host load”. It’s all about the number of URLs Googlebot can and wants to crawl.
Bot crawling is the first step in a series of complex tasks to get your pages seen on the first page of Google.
You must ensure that all your designated web properties are crawlable and that servers, pages and discoverable assets contain no unwanted search engine blocks. And, your information should be made available in text format which is what search engines still use.
You must also host your pages on a fast and scalable server infrastructure. A low crawl rate may indicate a low-quality site and will not get the “love” you need.
Essentially, you must allow the search engine bots (robots, spiders, crawlers) to access your designated content. The bot software should easily access, crawl and subsequently store (index) your information in their databases. Crawling typically occurs faster / deeper on high PageRank URLs, but other signals affect it as well.
The information you want search engines and users to find will be pulled and ranked instantly from these collected data sets.
Here are important considerations in this debate:
Does A Website Size Matter For Crawling?
If you have a website and assets that are low in count, you must still ensure crawlers can easily access these, but you will not need to focus on crawl budgets in the same way larger sites must. It’s all about balancing crawler frequency, crawler scope and server performance.
What Is A Robots.txt File For Controlling Spiders?
This is a text file, case sensitive: ‘robots.txt’ – that is stored at the root of your domain name location. You can access it by entering www.domain-name.com/robots.txt. You can block unwanted URLs, directories and file types. It can really help with duplicate content URL control and aids in strategically thinking about how bots (and users) can access your information.
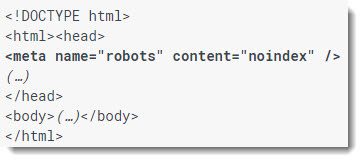
Should I Use The noindex Meta Tag?
This is a meta robots tag that is placed inside your page(s). It’s great for conditional restriction of crawling or indexation, whereas robots.txt is typically easier to manage for URL patterns. If you are blocking a page with robots and then apply noindex to the same page it will not see it. However, a noindex tag applied on verified pages (for index exclusion) is a viable strategy for most webmasters. Search results will not show a “Cached” link when used appropriately. While a robots.txt exclusion may still show pages in the search index, a “noindex” will not. (…just wait until the bot has visited the page, and it will be gone. Or, you can remove it inside GSC (below), which is faster).
Can I Use Google Search Console (GSC) for Crawl Diagnostics?
Make sure to have Google Search Console (Google Webmasters) configured for your website. It’s like having a (free) 24x7x365 web doctor listening and watching your entire “body” at regular intervals. The tool provides many key data metrics to help you.
Pages must render properly
You must make sure pages don’t send negative signals to the rest of the site (error pages, on-site duplicate content, hacked pages, etc.). Redirection with a 301 header status can solve many of these problems. You can see these ‘problem pages’ inside GSC.
For example, if you have a large amount of “page not found” – you might leave them alone, but more often you can a) create an actual 404 page and provide logical navigation and content to help the user, and/or b) 301 redirect to the relevant pages or previous URLs (if you are doing a web migration for example) that were working before.
NOTE: Review data in Google analytics to see if these are (look at a wide range in the date history) heavily trafficked pages. Make sure to also look at conversion metrics.
Another tip to control ‘page dups and orphaned pages’ is to verify and provide the actual number of pages for bot management. Begin by using the ‘site:’ command in Google. Numbers are not exact, but it returns how many pages are seen in the index at that time. Compare those pages to your actual pages in your CMS or e-commerce system (actual pages, not product filters) and within the Google Search Console tool. It’s important to consider issues with faceted navigation and parameterized URLs (session ID’s) as well.
The difficult and laborious task of building incoming links should be a consistent behavior on your team.
Check the “Links to Your Site” section under “Search Traffic” inside GSC.
Can I use Server Logs To Optimize My Website?
Download daily, weekly and monthly logs and scan them using desktop log analysis tools to get more details than analytics can provide.
There are massive amounts of significant data to help you optimize what you may have missed before.
You’ll access all the URLs that the various bots crawl on your site. Sort and filter by non 200 and 301 header codes to start and fix obvious page errors and redirect issues. Many advanced SEOs will use server logs, and you should too.
Do Redirect Chains Affect Crawling?
These pesky redirect chains are not visible to users, but can be a nuisance over time, and especially on large websites. Search engines must deal with them.
If you are going through a web migration, moving to SSL, or digging into historical data, or upgrading your URL structure (including use of trailing slashes or not) – it’ll be something you’ll want to address. You want short and concise 301 redirects.
What Are Common Filetypes That Google Can Index?
While the list below is usable for crawling, try to stay within recommended guidelines: Create & submit content that is text-based. (reference)
While Google enjoys major market penetration globally, all search engines crawl pure text based assets. You can use rich media, but make sure to add specific meta information via text as much as possible.
For example, you may have a relevant and educational YouTube video. Since Google cannot crawl the video, ensure that all meta data is provided in text format.
If you are embedding a video on your blog, provide rich text around it – within the body of your page content, including a link to it on YouTube.
If Google search results pages display video results for a query, you may be showing up next…once you have optimized it.
How To Find Filetypes In Google?
Do you wish to find certain filetypes in search? When you search in Google using advanced search operators – and with the filetype: search operator, you can filter by filetypes. Alternatively, you can find terms within them. Its basic construct looks like this – filetype:doc [term].
Here’s an example of finding Powerpoint files with a specific term: affordable health care act filetype:ppt (copy)
List of Filetypes:
- Adobe Flash (.swf)
- Adobe Portable Document Format (.pdf)
- Adobe PostScript (.ps)
- Autodesk Design Web Format (.dwf)
- Google Earth (.kml, .kmz)
- GPS eXchange Format (.gpx)
- Hancom Hanword (.hwp)
- HTML (.htm, .html, other file extensions)
- Microsoft Excel (.xls, .xlsx)
- Microsoft PowerPoint (.ppt, .pptx)
- Microsoft Word (.doc, .docx)
- OpenOffice presentation (.odp)
- OpenOffice spreadsheet (.ods)
- OpenOffice text (.odt)
- Rich Text Format (.rtf)
- Scalable Vector Graphics (.svg)
- TeX/LaTeX (.tex)
- Text (.txt, .text, other file extensions), including source code in common programming languages:
- Basic source code (.bas)
- C/C++ source code (.c, .cc, .cpp, .cxx, .h, .hpp)
- C# source code (.cs)
- Java source code (.java)
- Perl source code (.pl)
- Python source code (.py)
- Wireless Markup Language (.wml, .wap)
- XML (.xml)
If this post was helpful, please share it!
NEED SOME HELP? Contact Us Here and schedule your time.Jon Rognerud and Chaosmap work with Fortune 500 companies, associations and entrepreneurs to create digital traffic strategies that scale up members, customers, leads and sales with profitable returns. Mr. Rognerud wrote a best-selling book (Buy On Amazon), “The Ultimate Guide To Optimizing Your Website” (Entrepreneur). Connect directly here.