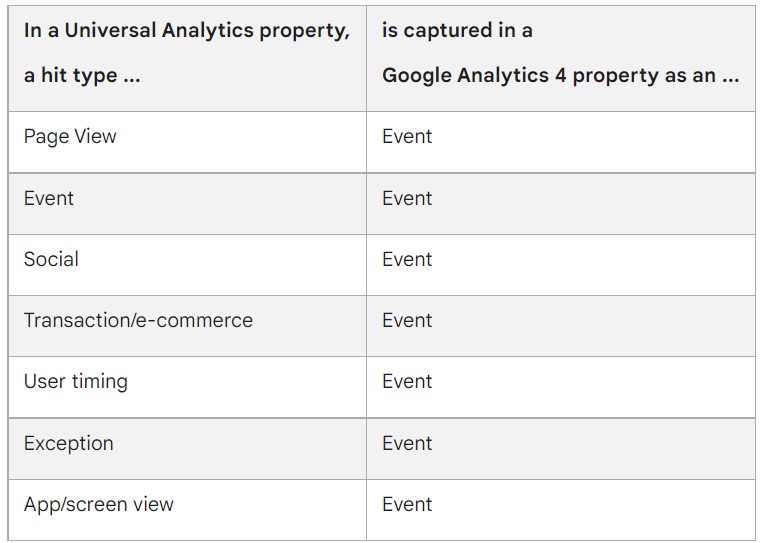
Google Analytics has significantly evolved since its Universal Analytics (UA) version, leading to the development and launch of the newest iteration: Google Analytics 4 (GA4).
We’ll also share an example coaching & consulting funnel where conversion points must be added along the customer journey. These conversion steps can easily be added inside GA4.
But first… here is the simple summary of the key differences between these two versions (GA & GA4), along with their respective pros and cons.
Universal Analytics (UA)
Pros:
- Matured Features: UA has a long-established set of features that are well-understood and widely adopted by marketers worldwide.
- Advanced Segmentation: Users can create advanced segments to analyze specific data subsets.
- Integration with Google Products: Seamless integration with Google Ads.
- Goal Completions: Allows setting up goals to track specific user interactions.
Cons:
- Limited Data Connectivity: It operates on a session-based model, which can limit the ability to connect data across platforms.
- Inability to Track Across Devices: Struggles to provide a unified customer view across multiple devices.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Pros:
- Event-based Tracking: GA4 shifted to an event-based tracking system, allowing more flexible and comprehensive data collection.
- Cross-platform Tracking: GA4 excels in unifying user experiences across different platforms and devices, providing a complete customer journey.
- AI-Powered Insights: GA4 leverages AI to provide automatic insights, including data trends and anomalies.
- Improved Audience Building: GA4’s analysis hub allows more sophisticated audience building and better integration with Google Ads.
Cons:
- Learning Curve: As it’s a new platform, marketers may need to invest time in understanding and mastering GA4.
- Incompatibility: Some existing UA features, like custom dimensions and metrics, don’t translate directly to GA4. (But you can create and customize once you learn how to).
- Limited Historical Data: GA4 doesn’t import historical data from UA, making it challenging to compare current data with older data.
IMPORTANT: For now, Google is still supporting both versions, and you can run them side by side. But, as of July 2023, GA Universal is no more, and you must have migrated over to GA4.
HERE IS AN EXAMPLE OF A CONVERSION TRACKING APPROACH for consultants, experts and professional services.
You need a funnel and the ability to track and report on each step:
In a traditional consulting funnel, conversion tracking is pivotal to understand how well your marketing efforts are working and to optimize your funnel for maximum conversions.
The transition from lead to application and then to booking/appointment is a journey that needs to be carefully monitored and optimized.
In Google Analytics 4 (GA4), there are several critical points to track, but the top three are:
1. Lead Generation: This is the first conversion point in your funnel. It involves tracking whenever a potential client shows interest in your services by filling out a form, subscribing to your newsletter, downloading a free resource, etc.
In GA4, this can be tracked as a custom event, where the action of form submission or resource download triggers the event.
It provides valuable insight into how effective your initial call to action and lead magnets are.
For any funnels that use Google ads (Search, YouTube), import these conversion points, track them, and feed data back to Google for your MQL’s and SQL’s.
2. Application Submission: The next crucial conversion point is when a lead submits an application or request for your consulting services.
The key here is to track not just the submission but also the quality of applications. Lead scoring is important for tracking, optimizing and preparing leads for the sales team.
In GA4, you can create a custom event for application submission and use event parameters to gather more information about the applicants, such as service they’re interested in, their industry, company size, and further qualification questions, etc.
3. Booking/Appointment Confirmation: This is the final conversion point where a lead can become a possible client by confirming a booking or appointment for the sales team (“the closers”).
You can track this in GA4 by setting up another custom event that triggers when a user completes the booking process.
This data helps you understand which marketing efforts are resulting in actual bookings and allows you to calculate your conversion rate from lead to client.
For each of these conversion points, you should also track the source or channel that the user came from (e.g., organic search, paid ad, social media, etc.)
This will provide valuable information about which channels are driving the most valuable conversions.
Remember, the goal is to use this data to optimize your funnel, improve your marketing ROI, and deliver a better user experience.
Regularly analyze your conversion data, look for trends and patterns, and make necessary adjustments to your strategy.
If you need help, reach out and connect with us here.
Jon Rognerud and Chaosmap work with Fortune 500 companies, small business and entrepreneurs to create digital traffic strategies that scale up customers, leads and sales with profitable returns. Mr. Rognerud wrote a best-selling book (Buy On Amazon), “The Ultimate Guide To Optimizing Your Website” (Entrepreneur). Connect directly here.